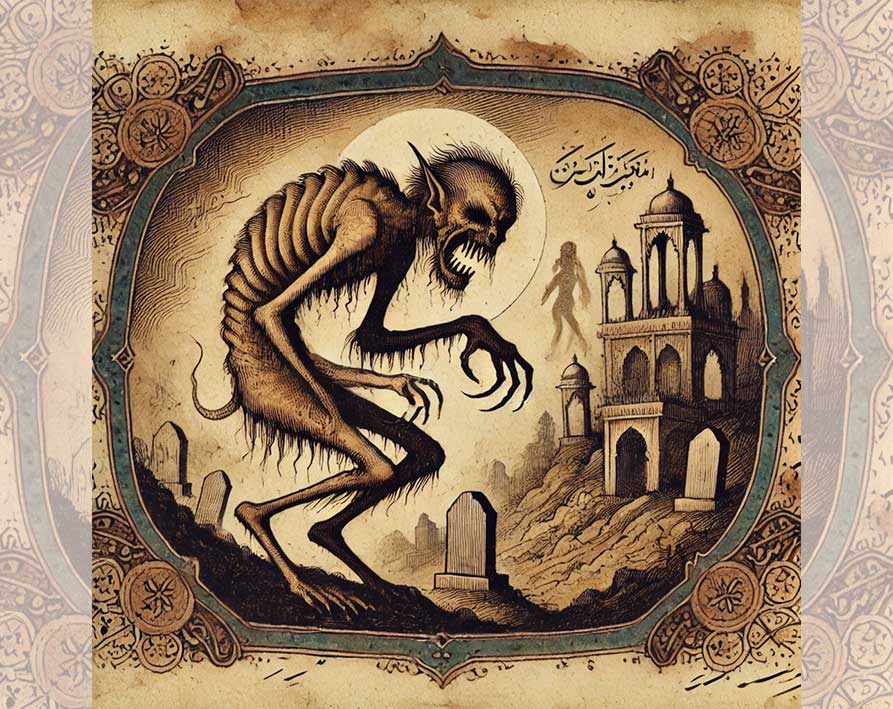
Ghul are monstrous Jinn who inhabit graveyards, ruins, and desolate places. Known for their cannibalistic nature, they lure travelers by shape-shifting into human forms — often women or children — only to attack and devour their victims.
Origin:
- Also known as: Ghoul
- Origin: Arabian mythology and pre-Islamic folklore
Key Figures:
Mother of Ghouls: In some stories, a matriarchal figure leads other Ghul in hunting and deception.
Themes:
- Death and Consumption: Ghul symbolize the fear of death, decay, and the unknown lurking in isolated places.
- Deception: Their shape-shifting highlights the danger of trusting strangers.
The Story:
A famous tale in One Thousand and One Nights tells of a prince who encounters a beautiful woman in the desert, only to realize too late that she is a Ghul in disguise, emphasizing the peril of misplaced trust.
Significance:
Ghul serve as dark reminders of death and the hidden threats within desolate places. They warn against both physical and emotional vulnerability.
Similar Tales:
- Si’lah: Both use trickery, though Ghul are more overtly violent.
Sources:
- One Thousand and One Nights
- Arabian folklore